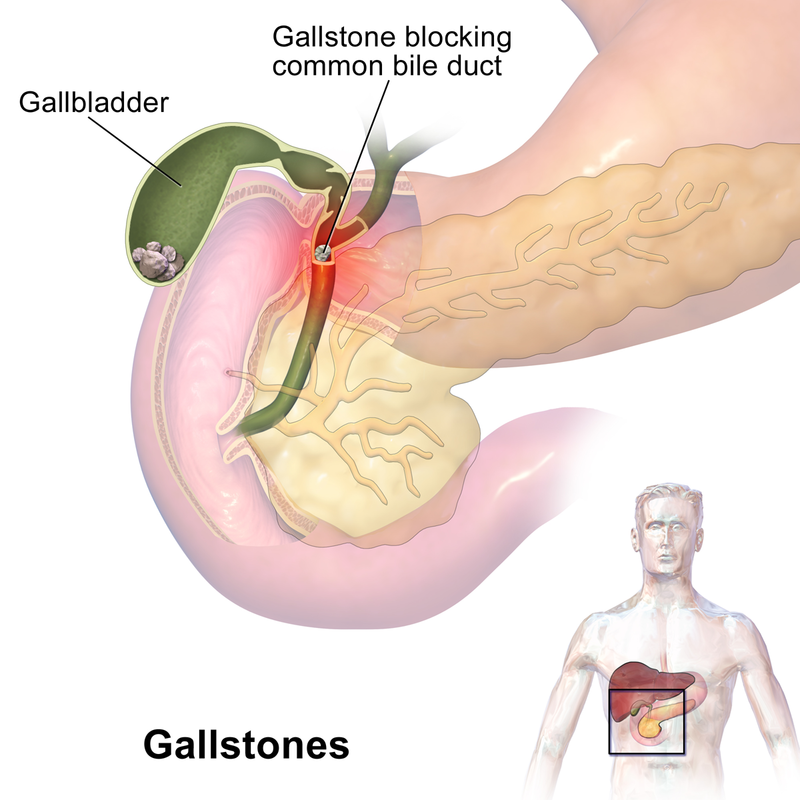
पित्ताशय की पथरी, जिसे पित्त पथरी के रूप में भी जाना जाता है, कठोर जमा होती है जो पित्ताशय में बनती है। वे आकार और संरचना में भिन्न हो सकते हैं, और मुख्य रूप से कोलेस्ट्रॉल या बिलीरुबिन से बने होते हैं। यहां पित्ताशय की पथरी के कारण, लक्षण और उपचार के बारे में कुछ जानकारी दी गई है:-
• कारण:-
1. अतिरिक्त बिलीरुबिन: पित्त में बिलीरुबिन का उच्च स्तर पित्त पथरी के निर्माण में योगदान कर सकता है। बिलीरुबिन एक पीला वर्णक है जो तब उत्पन्न होता है जब यकृत लाल रक्त कोशिकाओं को तोड़ता है।
2. अतिरिक्त कोलेस्ट्रॉल: जब लीवर द्वारा निर्मित पित्त में बहुत अधिक कोलेस्ट्रॉल होता है, तो यह पित्त पथरी का निर्माण कर सकता है।
3. गॉलब्लैडर डिसफंक्शन: गॉल ब्लैडर में सूजन (कोलेसिस्टाइटिस) या गॉल ब्लैडर की गतिशीलता में कमी जैसी कुछ स्थितियां पित्त पथरी के विकास के जोखिम को बढ़ा सकती हैं।
4. कंसन्ट्रेटेड बाइल: अगर गॉल ब्लैडर सही तरीके से खाली नहीं होता है या अगर यह बार-बार खाली नहीं होता है, तो बाइल गाढ़ा हो जाता है और गॉलस्टोन्स का निर्माण कर सकता है।
5. मोटापा: अधिक वजन या मोटापा होने से पित्त पथरी होने का खतरा बढ़ जाता है।
6. पारिवारिक इतिहास: पित्त पथरी का पारिवारिक इतिहास किसी व्यक्ति को उन्हें विकसित करने के लिए प्रेरित कर सकता है।
• लक्षण:-
1. मतली और उल्टी: पित्त पथरी से संबंधित दर्द के साथ मतली और उल्टी हो सकती है।
2. पेट दर्द: पित्ताशय की पथरी का सबसे आम लक्षण ऊपरी दाएं पेट में या पेट के केंद्र में अचानक और तीव्र दर्द होता है, जिसे पित्त शूल के रूप में जाना जाता है। यह दर्द कुछ मिनटों से लेकर कई घंटों तक रह सकता है।
3. पीठ दर्द: दर्द पीठ या कंधे के ब्लेड के बीच में विकीर्ण हो सकता है।
4. अपच और गैस: पित्त पथरी वाले कुछ लोग अपच, सूजन और अत्यधिक गैस का अनुभव करते हैं।
5. पीलिया: यदि पित्त पथरी पित्त नली को अवरुद्ध कर देती है, तो इससे त्वचा और आंखों का पीलापन (पीलिया) हो सकता है।
• इलाज:-
1. जीवनशैली में बदलाव: एक स्वस्थ जीवन शैली अपनाना, जिसमें संतुलित आहार बनाए रखना, यदि आवश्यक हो तो वजन कम करना और तेजी से वजन घटाने से बचना शामिल है, पित्त पथरी के जोखिम को कम करने में मदद कर सकता है।
2. दवाएं: कोलेस्ट्रॉल-आधारित पित्त पथरी को भंग करने के लिए कुछ दवाओं का उपयोग किया जा सकता है, लेकिन यह दृष्टिकोण आमतौर पर उन व्यक्तियों के लिए आरक्षित है जो सर्जरी के लिए उपयुक्त उम्मीदवार नहीं हैं।
3. सर्जरी: रोगसूचक पित्त पथरी के लिए सबसे आम उपचार पित्ताशय की थैली का सर्जिकल निष्कासन है, जिसे कोलेसिस्टेक्टोमी के रूप में जाना जाता है। यह पारंपरिक ओपन सर्जरी या न्यूनतम इनवेसिव लैप्रोस्कोपिक तकनीकों का उपयोग करके किया जा सकता है।
4. एंडोस्कोपिक प्रक्रियाएं: कुछ मामलों में, एंडोस्कोपिक तकनीकों का उपयोग करके पित्त पथरी को हटाया जा सकता है, जैसे कि एंडोस्कोपिक रेट्रोग्रेड कोलेजनोपैंक्रेटोग्राफी (ईआरसीपी) या परक्यूटेनियस ट्रांसहेपेटिक कोलेजनियोग्राफी (पीटीसी)।
5. सतर्क प्रतीक्षा: ऐसे मामलों में जहां पित्त पथरी छोटी और स्पर्शोन्मुख होती है, डॉक्टर तत्काल हस्तक्षेप के बिना स्थिति की निगरानी करने की सलाह दे सकते हैं।
“व्यक्तिगत परिस्थितियों के आधार पर सटीक निदान और उचित उपचार विकल्पों के लिए स्वास्थ्य देखभाल पेशेवर से परामर्श करना महत्वपूर्ण है।”
Gallbladder stones, also known as gallstones, are hardened deposits that form in the gallbladder. They can vary in size and composition and are primarily made up of cholesterol or bilirubin. Here’s some information on the causes, symptoms, and treatment of gallbladder stones:
Causes: –
1. Excess Cholesterol: When the bile produced by the liver contains too much cholesterol, it can lead to the formation of gallstones.
2. Excess Bilirubin: High levels of bilirubin in the bile can contribute to the formation of gallstones. Bilirubin is a yellow pigment that is produced when the liver breaks down red blood cells.
3. Concentrated Bile: If the gallbladder does not empty properly or if it doesn’t empty frequently enough, the bile becomes concentrated and can lead to the formation of gallstones.
4. Gallbladder Dysfunction: Certain conditions, such as gallbladder inflammation (cholecystitis) or impaired gallbladder motility, can increase the risk of developing gallstones.
5. Obesity: Being overweight or obese increases the risk of developing gallstones.
6. Family History: A family history of gallstones can predispose an individual to develop them.
Symptoms: –
1. Abdominal Pain: The most common symptom of gallstones is sudden and intense pain in the upper right abdomen or in the center of the abdomen, known as biliary colic. This pain can last from a few minutes to several hours.
2. Nausea and Vomiting: Gallstone-related pain can be accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
3. Jaundice: If a gallstone blocks the bile duct, it can lead to yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice).
4. Back Pain: Pain may radiate to the back or between the shoulder blades.
5. Indigestion and Gas: Some people with gallstones experience indigestion, bloating, and excessive gas.
Treatment: –
1. Watchful Waiting: In cases where gallstones are small and asymptomatic, the doctor may recommend monitoring the condition without immediate intervention.
2. Medications: Certain medications can be used to dissolve cholesterol-based gallstones, but this approach is typically reserved for individuals who are not suitable candidates for surgery.
3. Surgery: The most common treatment for symptomatic gallstones is surgical removal of the gallbladder, known as cholecystectomy. It can be done using traditional open surgery or minimally invasive laparoscopic techniques.
4. Endoscopic Procedures: In some cases, gallstones can be removed using endoscopic techniques, such as endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) or percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography (PTC).
5. Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including maintaining a balanced diet, losing weight if necessary, and avoiding rapid weight loss, can help reduce the risk of gallstone formation.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options based on individual circumstances.
